

As against this, radiation indicates how heat travels through places having no molecules. Conduction shows, how heat is transferred between objects in direct contact, but Convection reflects how heat travels through liquids and gases.Radiation is the heat transfer mechanism, in which the transition takes place through electromagnetic waves. Convection is the principle, wherein heat is transmitted by currents in a fluid, i.e. Conduction is a process in which heat is transported between parts of a continuum, through direct physical contact.The substantial differences between conduction, convection and radiation are explained as under: Key Differences Between Conduction, Convection and Radiation The best example of radiation is solar energy that we get from the sun, even though, it is miles aways from us. Radiant energy is capable of travelling in the vacuum from its source to the cooler surroundings. Hot objects generally emit thermal energy to cooler surroundings. In this process, the energy is transmitted through electromagnetic waves called as radiant energy.
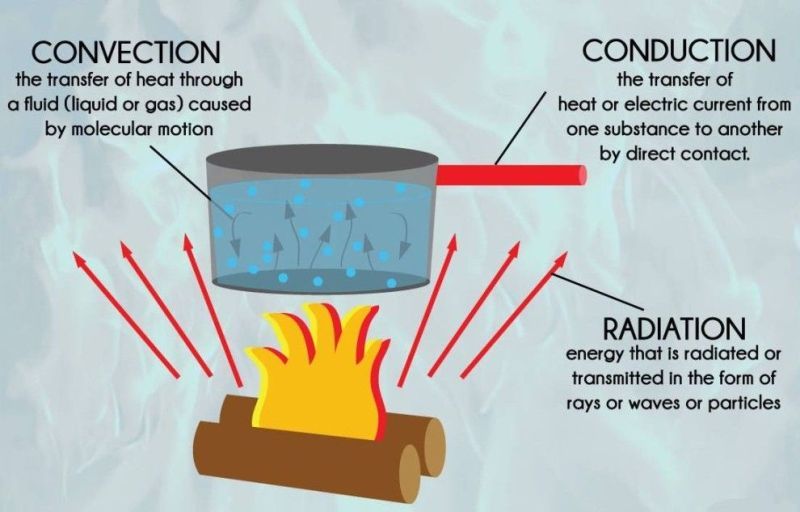
are some of the surface properties on which radiation depends greatly. Moreover, colour, surface orientation, etc. Whenever you feel heat without actually touching the object, it is because of radiation. The object need not be in direct contact with one another to transmit heat. It refers to the movement of heat in waves, as it does not need molecules to travel through. The heat transfer mechanism in which no medium is required is called radiation. When the convection is performed forcefully, the substance is compelled to move upwards by any physical means such as the pump. In convection, on heating up the substance, it’s molecules disperse and moves apart. Due to buoyancy, the hotter substance rises as it is less dense and the colder substance replaces it by sinking at the bottom, due to high density, which when gets hot moves upward, and the process continues. Gravity has a great role to play in natural convection such that when the substance is heated from below, leads to the expansion of the hotter part. Fluid alludes to any substance, whose molecules move freely from one place to another, such as liquid and gases. In science, Convection implies the form of heat transfer, by real movement of matter, that occurs only in fluids. Further, the objects which permit heat to travel easily through them are called conductors. In simple terms, whenever two objects are in direct contact with one another, there will be a transfer of heat from the hotter object to the colder one, which is due to conduction. The molecules collide with surrounding molecules, making them vibrate too, resulting in the transportation of thermal energy to neighbouring part of the object. It happens when the temperature of the molecules present in a substance increase, resulting in vigorous vibration. Occurs at a distance and does not heats the intervening substance.Ĭonduction can be understood as the process, which enables direct transfer of heat through the matter, due to the difference in temperature, between adjacent parts of the object. Occurs in fluids, by actual flow of matter.

Occurs in solids, through molecular collisions. Occurs from all objects, at temperature greater than 0 K. How heat travels between objects in direct contact. Radition alludes to the mechanism in which heat is transmitted without any physical contact between objects. Content: Conduction Vs Convection Vs RadiationĬonduction is a process in which transfer of heat takes place between objects by direct contact.Ĭonvection refers to the form of heat transfer in which energy transition occurs within the fluid. To study the difference between conduction, convection and radiation, let’s take a look at the article provided below. People often misconstrue, these forms of heat transfer but, they are based on diverse physical interaction to transfer energy. So, heat is the transition of energy from one system to another, due to the difference in temperature, which occurs in three different ways, that are conduction, convection and radiation. The conversion of matter from one state to another is termed as a change in state, that takes place due to the exchange of heat between the matter and its surroundings. The matter is present around us, in three states, solid, liquid and gas.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
